Embedding Bokeh plots with Github Pages
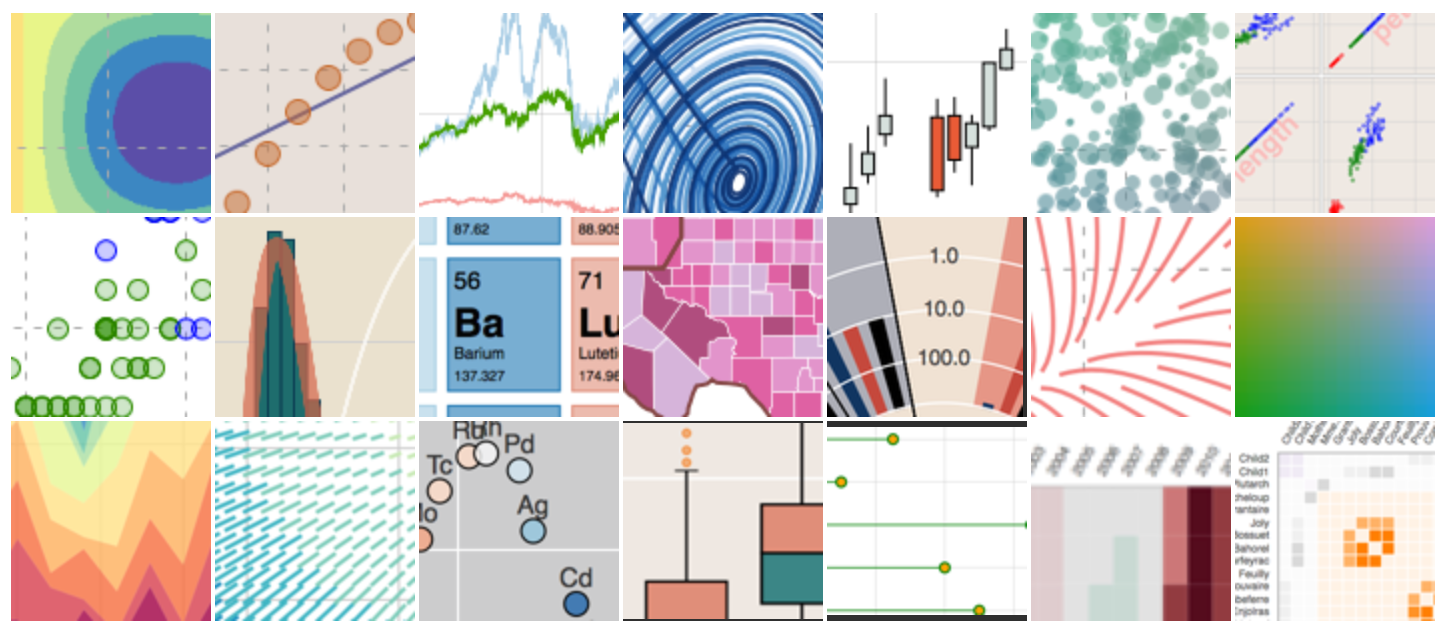
From bokeh.pydata.org:
Bokeh is a Python interactive visualization library that targets modern web browsers for presentation. Its goal is to provide elegant, concise construction of novel graphics in the style of D3.js, and to extend this capability with high-performance interactivity over very large or streaming datasets. Bokeh can help anyone who would like to quickly and easily create interactive plots, dashboards, and data applications.
This is a quick guide to embedding your visualizations in a Jekyll-hosted site, such as a Github Pages blog.
- Method 1: Embedding a single plot at a time with output_file()
- Method 2: Embedding 1 or more plots with components()
- Diagnosing possible errors
Method 1: Embedding a single plot at a time with output_file()
By far the simplest option is to use the output_file() function to produce a single HTML document.
For this demo, I’ll use a slightly modified version of a classic example in the Bokeh documentation, Iris.py.
import pandas as pd
from bokeh.sampledata.iris import flowers
from bokeh.plotting import figure, show, output_file
from bokeh.models import ColumnDataSource, HoverTool
colormap = {'setosa': 'red', 'versicolor': 'green', 'virginica': 'blue'}
flowers['colors'] = [colormap[x] for x in flowers['species']]
hover = HoverTool(tooltips=[
("Sepal length", "@sepal_length"),
("Sepal width", "@sepal_width"),
("Petal length", "@petal_length"),
("Species", "@species")
])
p = figure(title = "Iris Morphology", plot_height=500, plot_width=500, tools=[hover, "pan,reset,wheel_zoom"])
p.xaxis.axis_label = 'Petal Length'
p.yaxis.axis_label = 'Petal Width'
p.circle('petal_length', 'petal_width', color='colors',
fill_alpha=0.2, size=10, source=ColumnDataSource(flowers))
output_file('flowers.html')
show(p)
This command produces a single HTML file. Save this file to your github pages directory. Looking at the root directory, mine will go:
+-- assets
--img
--Bokeh
--flowers.html
Finally, inline in your markdown file, insert an <iframe></iframe> tag, like the example below:
<iframe src="/assets/img/Bokeh/flowers.html"
sandbox="allow-same-origin allow-scripts"
width="100%"
height="500"
scrolling="no"
seamless="seamless"
frameborder="0">
</iframe>
When you serve the website locally using Jekyll or post to Github Pages, your plot should be nicely embedded, interactive elements and all, as seen below:
This system works with embedding multiple files in different locations on your page, simply include a <iframe> tag for each plot.
Method 2: Embedding 1 or more plots with components()
Ths method, my preferred approach, leverages the includes functionality of Jekyll.
For this demo, I’ll use the same Iris.py version I used above, as well as bar_colormapped.py, another demo from the Bokeh documentation.
from bokeh.palettes import Spectral6
from bokeh.transform import factor_cmap
fruits = ['Apples', 'Pears', 'Nectarines', 'Plums', 'Grapes', 'Strawberries']
counts = [5, 3, 4, 2, 4, 6]
source = ColumnDataSource(data=dict(fruits=fruits, counts=counts))
q = figure(x_range=fruits, plot_height=350, toolbar_location=None, title="Fruit Counts")
q.vbar(x='fruits', top='counts', width=0.9, source=source, legend="fruits",
line_color='white', fill_color=factor_cmap('fruits', palette=Spectral6, factors=fruits))
q.xgrid.grid_line_color = None
q.y_range.start = 0
q.y_range.end = 9
q.legend.orientation = "horizontal"
q.legend.location = "top_center"
With both p (Iris visualization) and q (colorbar visualization) in memory, run:
from bokeh.embed import components
script, div = components([p, q])
print script, div[0], div[1]
Components is a function that returns only the <script> and <div> tags that we saw in the HTML file produced by output_file(). These plus a few stylesheet links are all that are required to actually generate the plots.
For this example, I only need the base styling from the documentation. These <link> and <script> tags, along with the <script> tag from components(), should be placed in a single HTML file in your _includes directory.
<link
href="https://cdn.pydata.org/bokeh/release/bokeh-0.12.13.min.css"
rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<script src="https://cdn.pydata.org/bokeh/release/bokeh-0.12.13.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
(function() {
...
}
</script>
In my case, I have it in:
+-- _includes
--custom
--bokeh_demo.html
I can simply use the Jekyll syntax {% include /custom/bokeh_demo.html %} to import the scripts at the top of my markdown document, and place the two <div> tags inline in markdown, wherever I want the plots to appear.
I can place standard markdown content between the div tags, to my heart’s delight.
Feel free to check out the raw markdown file used to generate this post for the code in action.
Diagnosing possible errors
- Consider removing the
<style></style>tag and its contents from the output_file() HTML, as that can sometimes cause issues in rendering<style> html { width: 100%; height: 100%; } body { width: 90%; height: 100%; margin: auto; } </style> - Check the Javascript function in the HTML file for a small syntax error:
console.log("Bokeh: ERROR: Unable to run BokehJS code because BokehJS library is missing") clearInterval(timer);Both of these lines should have a semicolon after them, so insert one after the
console.log()call. - If your page is served via HTTPS (as Github Pages is), verify that the stylesheet/script links are also HTTPS addresses, and if not simply replace “http” with “https” in the generated URLs.